Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy
A |
B |
C |
D |
E |
F |
G |
H |
I |
J |
K |
L |
M |
N |
O |
P |
Q |
R |
S |
T |
U |
V |
W |
X |
Y |
Z
Inconsistent Mathematics
Inconsistent mathematics is the study of the mathematical theories
that result when classical mathematical axioms are asserted within the
framework of a (non-classical) logic which can tolerate the presence
of a contradiction without turning every sentence into a theorem.
Inconsistent Mathematics began historically with foundational
considerations. Set-theoretic paradoxes such as Russell's led to
attempts to produce a consistent set theory as a foundation for
mathematics. But, as is well known, set theories such as ZF, NBG and
the like were in various ways ad hoc. Hence, a number of people
including da Costa (1974), Brady (1971), Priest, Routley, and Norman
(1989), considered it preferable to retain the full power of the
natural abstraction principle (every predicate determines a set), and
tolerate a degree of inconsistency in set theory. This requires, of
course, that one dispense with the logical principle ex
contradictione quodlibet (ECQ) (from a contradiction every
proposition may be deduced), as well as any principle which leads to
it, such as disjunctive syllogism (DS) (from A-or-B and not-A deduce
B). But considerable debate, in Burgess (1981) and Mortensen (1983),
made it clear that dispensing with ECQ and DS was not so
counter-intuitive, especially when a plausible story emerged about the
special conditions under which they continue to hold.
In addition, mathematics has a metalanguage; that is, names for
mathematical statements and other parts of syntax, self-reference,
proof and truth. Godel's contribution to the philosophy of
mathematics was to show that the first three of these can be
rigorously expressed in arithmetical theories, albeit in theories
which are either inconsistent or incomplete. The possibility of a
well-structured example of the former alternative was not taken
seriously, again because of belief in ECQ. However, in addition
natural languages seem to have their own truth predicate. Combined
with self-reference this produces the Liar paradox, "This sentence is
false", an inconsistency. Priest (1987) and Priest, Routley, and
Norman (1989) argued that the Liar had to be regarded as a statement
both true and false, a true contradiction. This represents another
argument for studying inconsistent theories, namely the claim that
some contradictions are true. Kripke (1975) proposed instead to model
a truth predicate differently, in a consistent incomplete theory. We
see below that incompleteness and inconsistency are closely related.
But mathematics is not its foundations. Hence there is a further
independent motive, to see what mathematical structure remains when
the constraint of consistency is relaxed. But it would be wrong to
regard this as in any way a loss of structure. If it is different at
all, then it represents an addition to known structure.
Robert K. Meyer (1976) seems to have been the first to think of an
inconsistent arithmetical theory. At this point, he was more
interested in the fate of a consistent theory, his relevant arithmetic
R#. There proved to be a whole class of inconsistent arithmetical
theories; see Meyer and Mortensen (1984), for example. Meyer argued
that these theories provide the basis for a revived Hilbert
Program. Hilbert's program was widely held to have been seriously
damaged by Godel's Second Incompleteness Theorem, according to which
the consistency of arithmetic was unprovable within arithmetic
itself. But a consequence of Meyer's construction was that within his
arithmetic R# it was demonstrable by simple finitary means that
whatever contradictions there might happen to be, they could not
adversely affect any numerical calculations. Hence Hilbert's goal of
conclusively demonstrating that mathematics is trouble-free proves
largely achievable. The arithmetical models used later proved to
allow inconsistent representation of the truth predicate. They also
permit representation of structures beyond natural number arithmetic,
such as rings and fields, including their order properties.
One could hardly ignore the examples of analysis and its special
case, the calculus. There prove to be many places where there are
distinctive inconsistent insights; see Mortensen (1995) for
example. (1) Robinson's non-standard analysis was based on
infinitesimals, quantities smaller than any real number, as well as
their reciprocals, the infinite numbers. This has an inconsistent
version, which has some advantages for calculation in being able to
discard higher-order infinitesimals. Interestingly, the theory of
differentiation turned out to have these advantages, while the theory
of integration did not. (2) Another place is topology, where one
readily observes the practice of cutting and pasting spaces being
described as "identification" of one boundary with another. One can
show that this can be described in an inconsistent theory in which the
two boundaries are both identical and not identical, and it can be
further argued that this is the most natural description of the
practice. (3) Yet another application is the class of inconsistent
continuous functions. Not all functions which are classically
discontinuous are amenable of inconsistent treatment; but some are,
for example f(x)=0 for all x<0 and f(x)=1 for all
x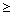 0. The inconsistent extension replaces the first
< by
0. The inconsistent extension replaces the first
< by 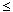 , and has distinctive structural
properties. These inconsistent functions may well have some
application in dynamic systems in which there are discontinuous jumps,
such as quantum measurement systems. Differentiating such functions
leads to the delta functions, applied by Dirac to the study of quantum
measurement also. (4) Next, there is the well-known case of
inconsistent systems of linear equations, such as the system (i)
x+y=1, plus (ii) x+y=2. Such systems can potentially arise within the
context of automated control. Little work has been done classically
to solve such systems, but it can be shown that there are well-behaved
solutions within inconsistent vector spaces. (5) Finally, one can note
a further application in topology and dynamics. Given a supposition
which seems to be conceivable, namely that whatever happens or is
true, happens or is true on an open set of (spacetime) points, one has
that the logic of dynamically possible paths is open set logic, that
is to say intuitionist logic, which supports incomplete theories par
excellence. This is because the natural account of the negation of a
proposition in such a space says that it holds on the largest open set
contained in the Boolean complement of the set of points on which the
original proposition held, which is in general smaller than the
Boolean complement. However, specifying a topological space by its
closed sets is every bit as reasonable as specifying it by its open
sets. Yet the logic of closed sets is known to be paraconsistent,
ie. supports inconsistent theories; see Goodman (1981) for example.
Thus given the (alternative) supposition which also seems to be
conceivable, namely that whatever is true is true on a closed set of
points, one has that inconsistent theories may well hold. This is
because the natural account of the negation of a proposition, namely
that it holds on the smallest closed set containing the Boolean
negation of the proposition, means that on the overlapping boundary
both the proposition and its negation hold. Thus dynamical theories
determine their own logic of possible propositions, and corresponding
theories which may be inconsistent, and are certainly as natural as
their incomplete counterparts.
, and has distinctive structural
properties. These inconsistent functions may well have some
application in dynamic systems in which there are discontinuous jumps,
such as quantum measurement systems. Differentiating such functions
leads to the delta functions, applied by Dirac to the study of quantum
measurement also. (4) Next, there is the well-known case of
inconsistent systems of linear equations, such as the system (i)
x+y=1, plus (ii) x+y=2. Such systems can potentially arise within the
context of automated control. Little work has been done classically
to solve such systems, but it can be shown that there are well-behaved
solutions within inconsistent vector spaces. (5) Finally, one can note
a further application in topology and dynamics. Given a supposition
which seems to be conceivable, namely that whatever happens or is
true, happens or is true on an open set of (spacetime) points, one has
that the logic of dynamically possible paths is open set logic, that
is to say intuitionist logic, which supports incomplete theories par
excellence. This is because the natural account of the negation of a
proposition in such a space says that it holds on the largest open set
contained in the Boolean complement of the set of points on which the
original proposition held, which is in general smaller than the
Boolean complement. However, specifying a topological space by its
closed sets is every bit as reasonable as specifying it by its open
sets. Yet the logic of closed sets is known to be paraconsistent,
ie. supports inconsistent theories; see Goodman (1981) for example.
Thus given the (alternative) supposition which also seems to be
conceivable, namely that whatever is true is true on a closed set of
points, one has that inconsistent theories may well hold. This is
because the natural account of the negation of a proposition, namely
that it holds on the smallest closed set containing the Boolean
negation of the proposition, means that on the overlapping boundary
both the proposition and its negation hold. Thus dynamical theories
determine their own logic of possible propositions, and corresponding
theories which may be inconsistent, and are certainly as natural as
their incomplete counterparts.
Category theory throws light on many mathematical structures. However,
when there are consistency problems for category theory as a
foundation for mathematics, which certainly has been proposed. Hence
there is the same possible application of inconsistent
solutions. There is also an important collection of categorial
structures, the toposes, which support open set logic in exact
parallel to the way sets support Boolean logic. This has been taken by
many to be a vindication of the foundational point of view of
mathematical intuitionism. However, it can be proved that that toposes
support closed set logic as readily as they support open set
logic. That should not be viewed as an objection to intuitionism,
however, so much as an argument that inconsistent theories are equally
reasonable as items of mathematical study.
Duality between incompleteness/intuitionism and
inconsistency/paraconsistency has at least two aspects. First there is
the above topological (open/closed) duality. Second there is Routley *
duality. Discovered by the Routleys (1972) as a semantical tool for
relevant logics, the * operation dualises between inconsistent and
incomplete theories of the large natural class of de Morgan
logics. Both kinds of duality interact as well, where the * gives
distinctive duality and invariance theorems for open set and closed
set arithmetical theories. On the basis of these results, it is fair
to argue that both kinds of mathematics, intuitionist and
paraconsistent, are equally reasonable.
These constructions do not in any way challenge or repudiate
existing mathematics, but extend our conception of what is
mathematically possible.
- Brady, Ross, "The Consistency of the Axioms of Abstraction
and Extensionality in a Three-Valued Logic", Notre Dame Journal of
Formal Logic (NDJFL), 12 (1971), 447-453.
- Burgess, John, "Relevance, a Fallacy?", NDJFL, 22 (1981),
97-104.
- Da Costa, Newton C.A. "On the Theory of Inconsistent Formal
Systems", NDJFL, 15 (1974), 497-510.
- Goodman, Nicholas, "The Logic of Contradictions", Zeitschrift
fur Mathematische Logic und Grundlagen der Arithmetik 27 (1981)
119-126.
- Kripke, Saul, "Outline of a Theory of Truth", The Journal of
Philosophy 72 (1975), 690-716.
- Meyer, Robert K., "Relevant Arithmetic", Bulletin of the
Section of Logic of the Polish Academy of Sciences, 5 (1976),
133-137.
- Meyer, Robert K. and Chris Mortensen, "Inconsistent Models for
Relevant Arithmetics",The Journal of Symbolic Logic, 49 (1984),
917-929.
- Mortensen, Chris, "Reply to Burgess and to Read", NDJFL
24 (1983), 35-40.
- Mortensen, Chris, Inconsistent Mathematics, Kluwer
Mathematics and Its Applications Series, Kluwer, 1995.
(Errata)
- Priest, Graham, In Contradiction, Dordrecht, Nijhoff, 1987.
- Priest, Graham, Richard Routley and Jean Norman (eds),
Paraconsistent Logic, Munchen, Philosophia Verlag, 1989.
- Routley, Richard and Val, "The Semantics of First Degree
Entailment", Nous, 6 (1972), 335-359.
mathematics, philosophy of | contradiction |
logic: paraconsistent
Copyright © 1996, 1997 by
Chris Mortensen
University of Adelaide
cmortens@arts.adelaide.edu.au
A |
B |
C |
D |
E |
F |
G |
H |
I |
J |
K |
L |
M |
N |
O |
P |
Q |
R |
S |
T |
U |
V |
W |
X |
Y |
Z
 Table of Contents
Table of Contents
First published: July 2, 1996
Content last modified: January 9, 1997
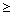 0. The inconsistent extension replaces the first
< by
0. The inconsistent extension replaces the first
< by 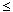 , and has distinctive structural
properties. These inconsistent functions may well have some
application in dynamic systems in which there are discontinuous jumps,
such as quantum measurement systems. Differentiating such functions
leads to the delta functions, applied by Dirac to the study of quantum
measurement also. (4) Next, there is the well-known case of
inconsistent systems of linear equations, such as the system (i)
x+y=1, plus (ii) x+y=2. Such systems can potentially arise within the
context of automated control. Little work has been done classically
to solve such systems, but it can be shown that there are well-behaved
solutions within inconsistent vector spaces. (5) Finally, one can note
a further application in topology and dynamics. Given a supposition
which seems to be conceivable, namely that whatever happens or is
true, happens or is true on an open set of (spacetime) points, one has
that the logic of dynamically possible paths is open set logic, that
is to say intuitionist logic, which supports incomplete theories par
excellence. This is because the natural account of the negation of a
proposition in such a space says that it holds on the largest open set
contained in the Boolean complement of the set of points on which the
original proposition held, which is in general smaller than the
Boolean complement. However, specifying a topological space by its
closed sets is every bit as reasonable as specifying it by its open
sets. Yet the logic of closed sets is known to be paraconsistent,
ie. supports inconsistent theories; see Goodman (1981) for example.
Thus given the (alternative) supposition which also seems to be
conceivable, namely that whatever is true is true on a closed set of
points, one has that inconsistent theories may well hold. This is
because the natural account of the negation of a proposition, namely
that it holds on the smallest closed set containing the Boolean
negation of the proposition, means that on the overlapping boundary
both the proposition and its negation hold. Thus dynamical theories
determine their own logic of possible propositions, and corresponding
theories which may be inconsistent, and are certainly as natural as
their incomplete counterparts.
, and has distinctive structural
properties. These inconsistent functions may well have some
application in dynamic systems in which there are discontinuous jumps,
such as quantum measurement systems. Differentiating such functions
leads to the delta functions, applied by Dirac to the study of quantum
measurement also. (4) Next, there is the well-known case of
inconsistent systems of linear equations, such as the system (i)
x+y=1, plus (ii) x+y=2. Such systems can potentially arise within the
context of automated control. Little work has been done classically
to solve such systems, but it can be shown that there are well-behaved
solutions within inconsistent vector spaces. (5) Finally, one can note
a further application in topology and dynamics. Given a supposition
which seems to be conceivable, namely that whatever happens or is
true, happens or is true on an open set of (spacetime) points, one has
that the logic of dynamically possible paths is open set logic, that
is to say intuitionist logic, which supports incomplete theories par
excellence. This is because the natural account of the negation of a
proposition in such a space says that it holds on the largest open set
contained in the Boolean complement of the set of points on which the
original proposition held, which is in general smaller than the
Boolean complement. However, specifying a topological space by its
closed sets is every bit as reasonable as specifying it by its open
sets. Yet the logic of closed sets is known to be paraconsistent,
ie. supports inconsistent theories; see Goodman (1981) for example.
Thus given the (alternative) supposition which also seems to be
conceivable, namely that whatever is true is true on a closed set of
points, one has that inconsistent theories may well hold. This is
because the natural account of the negation of a proposition, namely
that it holds on the smallest closed set containing the Boolean
negation of the proposition, means that on the overlapping boundary
both the proposition and its negation hold. Thus dynamical theories
determine their own logic of possible propositions, and corresponding
theories which may be inconsistent, and are certainly as natural as
their incomplete counterparts.
 Table of Contents
Table of Contents